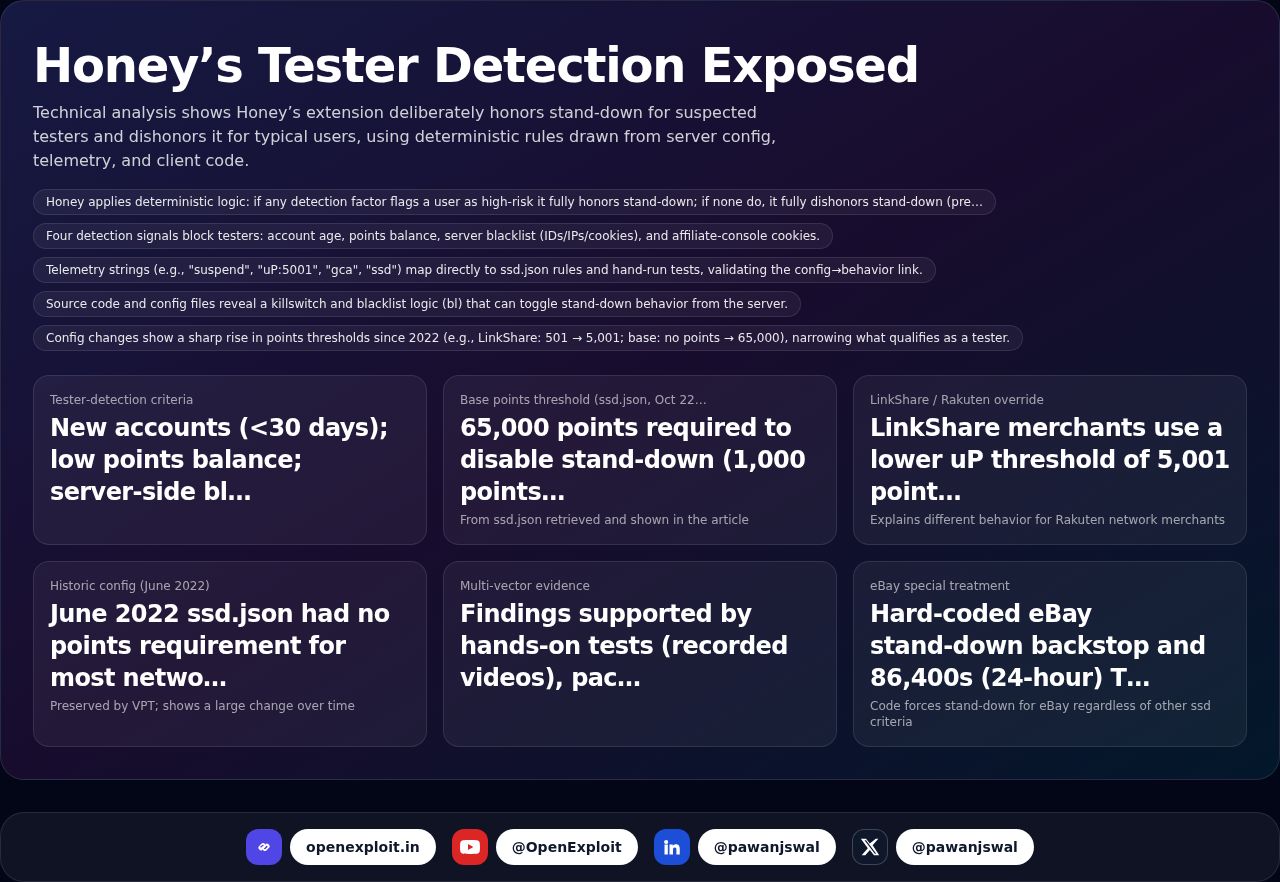
What Is 2FA? And Why You Should Use It Everywhere

In an age where everything from our bank accounts to our family photos exists online, guarding our online identity has never been more crucial. Passwords once were sufficient to secure our accounts, but not anymore. Hackers are cleverer, phishing scams are rampant, and data breaches occur nearly every day. So, how do we stay one step ahead and safeguard our online existence?
The solution: Two-Factor Authentication, or 2FA.
In this blog post, we'll summarize what two-factor authentication is, how it functions, and why you should have it enabled on all accounts that provide it.
What is Two-Factor Authentication?
Let's begin at the beginning.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security mechanism that asks for two distinct kinds of information in order to confirm your identity when logging into an account.
Imagine it this way: entering your home typically takes one key (your password). But with 2FA, even if someone has your key, they still must provide a second type of evidence—such as a fingerprint or a code texted to your phone—to enter.
In more technical language, 2FA employs two of the following three "factors":
- Something you know – such as a password or PIN.
- Something you possess – such as your phone, a security token, or one-time code.
- Something you are – such as your voice, face, or fingerprint (biometrics).
By asking for two of those, 2FA makes it extremely difficult for hackers to log into your account—even if they have your password.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
Let's go through an easy example.
Imagine you’re logging into your email. Normally, you’d enter your username and password. With 2FA turned on, you’ll also need to do one more thing:
- Enter a code sent to your phone via SMS or an app like Google Authenticator.
- Approve the login through a push notification on your device.
- Insert a USB security key and tap it.
- Scan your fingerprint or use Face ID.
This additional step only requires a few seconds, but it provides a strong added layer of security. Even if someone steals or guesses your password, they won't be able to access your account without that second factor.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
There are a few different methods of 2FA, and the one you use might depend on the device or service:
SMS or Email Codes
You are sent a temporary code by text message or email that you input after you enter your password. It's more secure than having no 2FA, but it's also the least secure because text messages and emails can be diverted or intercepted by hackers.
Authentication Apps
Apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy create time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) on a 30-second basis. These apps are more secure than SMS and function even if your phone is not connected to the internet.
Push Notifications
Certain services (such as Duo or Apple ID) send a push notification to your phone. You simply tap "Yes" or "Approve" to sign in. It's quick, secure, and convenient.
Hardware Security Keys
These are physical objects (such as YubiKey or Google Titan) you insert into your computer or tap against your phone to verify. They provide the most secure type of 2FA and can be nearly unbreachable to hacking.
Biometrics
Employing your fingerprint, face, or voice as the second factor is getting more widespread, particularly on your phone. It's handy but not necessarily a choice available with all services.
Why You Should Use 2FA Everywhere
You might be thinking: "I use strong passwords—do I truly need 2FA?"
The answer is, yes. Here's why:
Passwords by themselves are no longer secure
Folks have a tendency to reuse passwords or select weak passwords. Even a strong, single-use password might be revealed within a data breach. With 2FA, an attacker would require both your password and use of your second factor—something they won't likely possess.
Data breaches occur continually
Even large corporations are hacked. When your password has been exposed in one hack, hackers also tend to try it on other sites. That is called credential stuffing. 2FA stops them dead in their tracks.
Secures Your Most Prized Accounts
Consider what trouble a person would be able to cause if they had access to your:
- Email (reset other account passwords)
- Bank or PayPal account
- Cloud storage (Google Drive, Dropbox)
- Social media (impersonation or fraud)
2FA will keep all that secure.
Peace of Mind
Having that extra protection on your accounts reassures you. Even if someone obtains your password, they still can't gain entry.
Where You Should Activate 2FA
You should activate 2FA wherever it's offered—particularly on high-value accounts such as:
- Email (Gmail, Outlook, etc.)
- Bank and financial apps
- Social media (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter/X)
- Cloud storage (Google Drive, iCloud, Dropbox)
- Work or school accounts
- Shopping sites (Amazon, eBay, etc.)
Most services have 2FA options in Account Settings or Security. It takes just a few minutes to configure.
Any Drawbacks?
2FA isn't flawless. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- If you lose your phone or device, it can be difficult to log in. That's why many services allow you to set up backup methods such as recovery codes.
- SMS 2FA can be compromised via SIM swapping or phishing, so attempt to use an authentication app or hardware key when possible.
- Some websites still do not have 2FA support (which is annoying), but most are catching up.
Those are tiny compromises for the huge security improvement, though.
Safe 2FA Tips
- Use an authentication app rather than SMS wherever you can.
- Note down recovery codes and keep them somewhere secure.
- Don't give your 2FA codes to anyone—like your password.
- Watch out for phishing scams that request your 2FA code or pressure you to authenticate a login.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity doesn't need to be difficult. In fact, enabling two-factor authentication is among the simplest and most powerful steps you can take to secure yourself online.
It takes only a few seconds to add to your login time—but those few seconds can keep you safe from a hacked account, stolen identity, or worse.
So when you next log in to your email, bank, or social media account, take a glance at your settings and turn on 2FA if it's an option.
You'll thank yourself later. Stay safe. Stay smart. And always double up on your security.