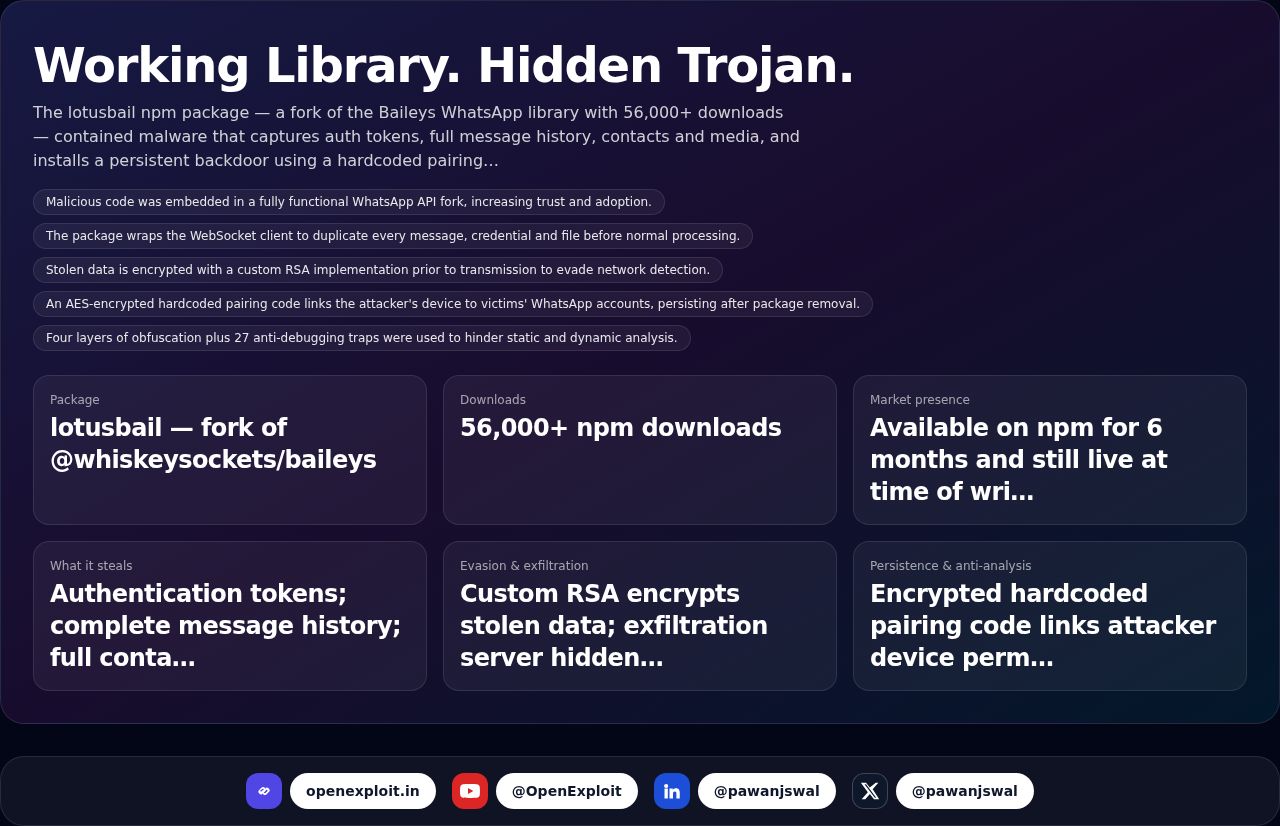
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity Defense

Cyber attacks are being increased with growing time, more intelligent, sophisticated, and hardly identifiable. In modern times, various cyber threats emerge, which could be zero-day vulnerabilities or some phishing mail; thus, security measures applied hitherto can no longer handle this job.
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI) — a game-changing tool in the fight against cyber threats. But how exactly does AI help in cybersecurity? And why is it becoming so important? In this blog post, we’ll break it down in simple terms and explore the critical role AI plays in modern cybersecurity defense.
Prefer watching instead of reading? Here’s a quick video guide
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Before diving into its role in cybersecurity, let’s quickly understand what AI is.
Artificial Intelligence refers to the capacity of a machine or system to emulate human intelligence. It involves learning from data, pattern recognition, decision-making, and even self-improvement over time.
In cybersecurity, AI is capable of scanning massive amounts of data, recognizing anomalous behavior, identifying threats, and even taking action quicker than a human can.
Why Do We Need AI in Cybersecurity?
Let's consider a big organization with thousands of devices, users, and servers. Each second, massive amounts of data are being created—login attempts, emails, file transfers, and more. Baked into that wave of activity could be a cyberattack.
Now, imagine a group of human analysts attempting to scan all that activity in real-time. It's simply not feasible. They'd be swamped.
That's where AI comes in. It can parse enormous amounts of data in real-time and determine threats much faster and more accurately than a human analyst.
How AI Benefits Cybersecurity Defense
Following are the major ways AI is changing cybersecurity:
Threat Detection and Prediction
AI will recognize threats by studying patterns in data. It employs machine learning (a form of AI) to discover what constitutes normal behavior and then alerts anything out of the ordinary.
For instance:
- If a user logs in unexpectedly from a different country at 3 AM, AI could mark it as suspicious.
- If an employee attempts to download gigabytes of data within a short time frame, AI would see it as a possible insider threat.
The more time passes, the more able the AI system is to discriminate between what potentially might be a genuine attack versus an unusual but benign activity.
Real-Time Response
AI has one of the greatest advantages as its speed. When an attack is identified, AI can:
- Block the suspicious action.
- Quarantine infected systems.
- Inform the security team in real time.
This is quick enough to prevent attackers before they can result in damage.
Malware Detection
Legacy antivirus is based on signatures — familiar patterns of malicious code. But attackers constantly evolve, and their methods leave them with polymorphic malware that shifts its form every time.
AI can transcend signature-based detection. It can evaluate what a file does and determine if it's behaving like malware — even if it's never encountered that particular threat before.
Phishing Detection
Phishing emails are becoming smarter and more difficult to detect. AI can inspect emails in real-time and detect phishing attempts based on:
- Typical phishing language or tone.
- Suspicious links or attachments.
- Defensive domain spoofing.
There are now some email security products that employ AI to help block or flag phishing emails even before they arrive in your user's inbox.
Security Automation
AI assists in automating tedious and time-consuming processes, such as:
- Investigating alerts.
- Correlating logs.
- Performing vulnerability scans.
This not only lightens the load for security teams but also lessens the likelihood of human error.
User Behavior Analytics (UBA)
Each user has a behavior pattern — when they log in, what apps they access, how much data they view. AI can create a profile for each user and mark out anything that's out of the ordinary.
For instance:
- If an employee in finance suddenly accesses engineering files.
- Or logs in during odd hours from various locations.
This is particularly useful for identifying insider threats or compromised accounts.
Real-World Examples
Google and Gmail
Google employs AI to reject over 100 million phishing attempts daily on Gmail. The AI system can detect known and unknown threats with astounding accuracy.
Darktrace
Darktrace is a cybersecurity firm that employs AI to watch network traffic and react to threats in real-time. Their AI algorithms learn the typical behavior of each user and device and can automatically block threats before harm is caused.
Challenges and Limitations
AI is strong, but it's not flawless. These are some of the challenges:
False Positives
Occasionally, AI may label innocent behavior as suspicious. Excessive false alarms can overwhelm analysts or cause undue disruptions.
Training Data
AI systems require plenty of good-quality data to learn effectively. If data is biased or incomplete, then the AI can make the wrong decisions.
Adversarial Attacks
Thieves are currently attempting to mislead AI systems by feeding them false information — a technique referred to as adversarial machine learning. It's similar to deceiving the AI that a threat is not a threat.
Complexity
Applying AI in cybersecurity needs experts, adequate infrastructure, and continuous calibration. Small businesses might find it difficult to embrace AI-driven tools.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
AI in cybersecurity is continuing to grow. Looking forward, we will see:
- Dumber self-healing systems that not only detect and react to attacks but also automatically patch vulnerabilities.
- Cooperating AI systems exchanging threat intelligence industries-wide.
- Cyber AI forensics, assisting investigators to track the source and path of attacks more efficiently.
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence is not a silver bullet, but it's an effective ally against cyber threats. While attacks become more sophisticated, AI provides the speed, scale, and intelligence that humans alone cannot achieve.
For business, students, and security enthusiasts alike, it is essential to know about AI's place in defense to remain competitive in this constantly evolving digital world. Whether you're developing security solutions or just securing your own information, AI is not something you can afford to overlook.