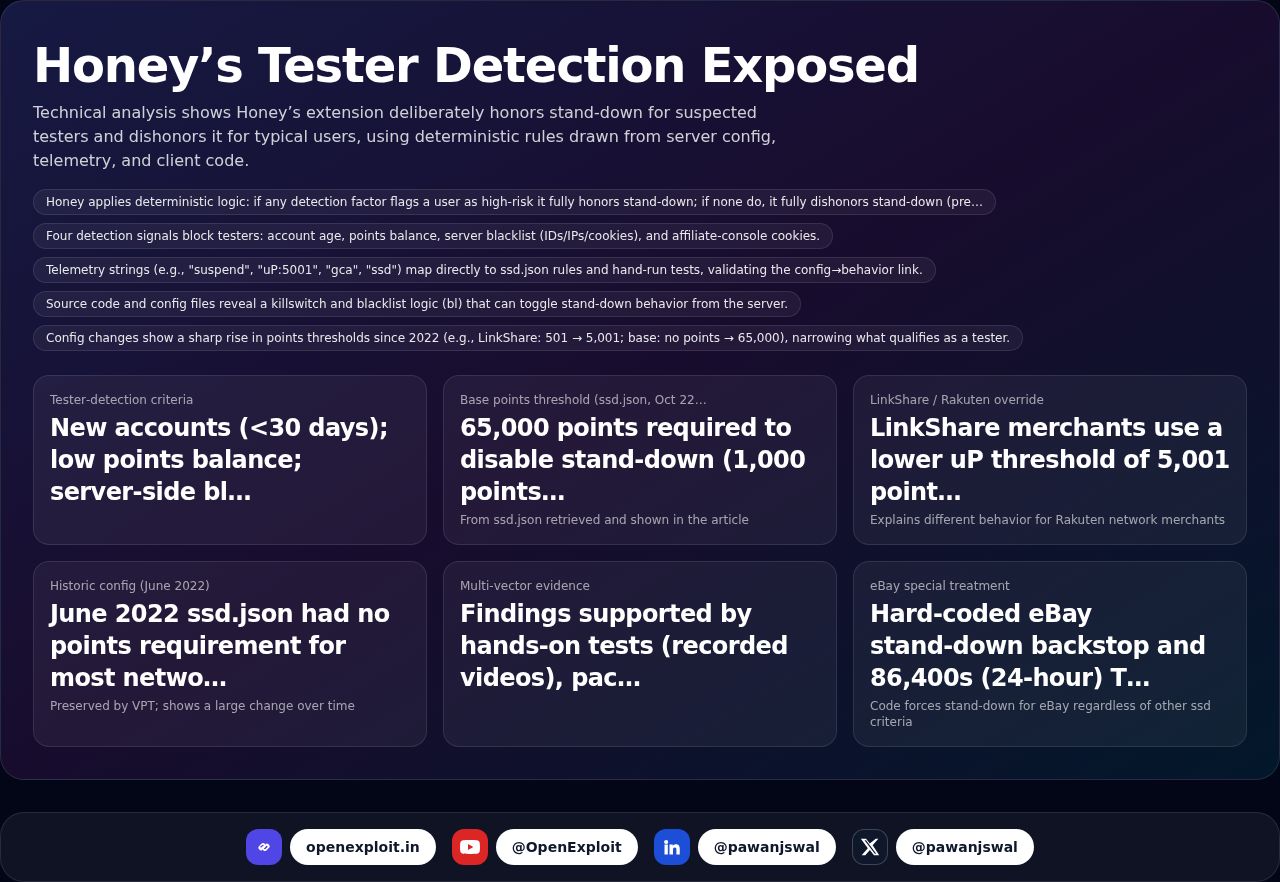
LangGrinch: LangChain Core CVE-2025-68664
A serialization bug in langchain-core allowed unescaped 'lc' markers to revive unsafe objects, enabling secret extraction and instantiation risks across common flows. Patches are released — update immediately.

A critical LangChain core bug can turn a single LLM prompt into a secret-exfiltration or object-instantiation exploit. If you run LangChain in production, this is urgent.
A serialization bug in langchain-core allowed unescaped 'lc' markers to revive unsafe objects, enabling secret extraction and instantiation risks across common flows. Patches are released — update immediately.
Source: Cyata — Source link
Highlights
| Metric | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CVE / Advisory | CVE-2025-68664 / GHSA-c67j-w6g6-q2cm | |
| Affected component | langchain-core dumps() / dumpd() serialization APIs | |
| Severity | CVSS 9.3 (Critical) | Categorized as CWE-502: Deserialization of Untrusted Data |
| Scale | ~847M total downloads; ~98M downloads in the last month | Public package telemetry cited (pepy.tech, pypistats) as of late December 2025 |
| Patches | Fixed in langchain-core versions 1.2.5 and 0.3.81 | Recommend immediate upgrade |
| Scope | 12 distinct vulnerable flows listed in the advisory | Includes streaming, logging, message history, caches and common integrative flows |
Key points
- dumps()/dumpd() failed to escape user-controlled dicts that include the 'lc' key, allowing them to be treated as LangChain objects on deserialization.
- An attacker-controlled LLM output (e.g., additional_kwargs or response_metadata) can be serialized then deserialized, enabling exploits triggered by a single prompt.
- loads()/loads() use an allowlist including langchain_core, langchain_openai, langchain_aws, etc.; some allowlisted classes perform network or file operations on instantiation.
- The prior default behavior allowed secret resolution from environment variables (secrets_from_env=true), enabling secret extraction during deserialization.
- Real-world impacts include secret exfiltration, unsafe object instantiation with side effects, and potential code execution via Jinja2 template rendering when templates are rendered later.
- Immediate mitigations: upgrade to patched versions, treat all LLM outputs as untrusted, review/disable automatic secret resolution, and audit serialization-deserialization paths.
- The same 'lc' marker confusion pattern was reported in LangChainJS (CVE-2025-68665), indicating the risk spans multiple ecosystems.
Timeline
- 2025-12-04 — Report submitted via Huntr
- 2025-12-05 — Acknowledged by LangChain maintainers
- 2025-12-24 — Advisory and CVE published
- 2025-12-25 — Article published on Cyata
Why this matters
Agent frameworks like LangChain are now critical infrastructure. A single reserved serialization marker and permissive defaults can expose environment secrets, trigger network/file side effects, or lead to code-execution paths — all at global scale given widespread installs. Fixing the library is necessary but not sufficient: organizations need inventory, safer defaults, and governance to ensure LLM outputs and serialized artifacts never cross trust boundaries unchecked.