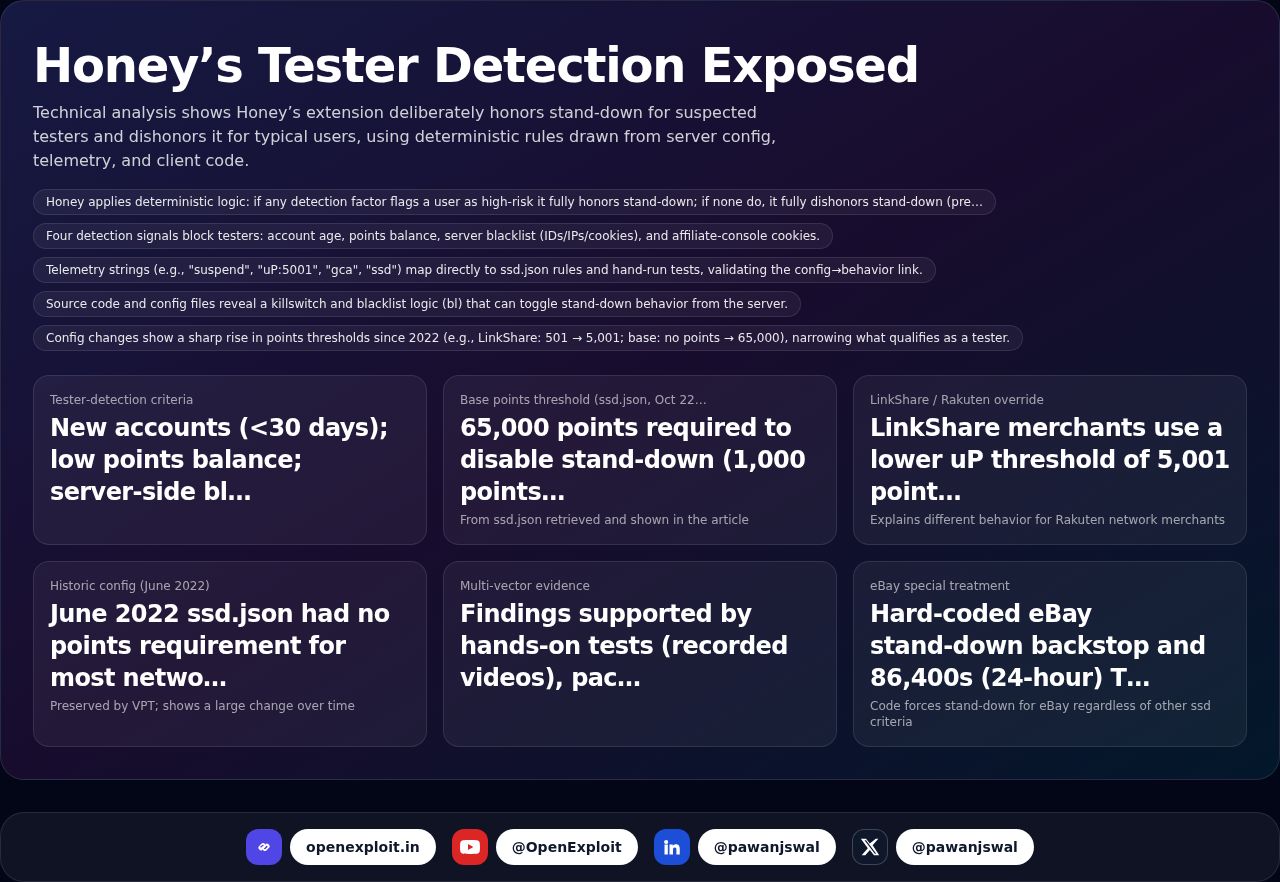
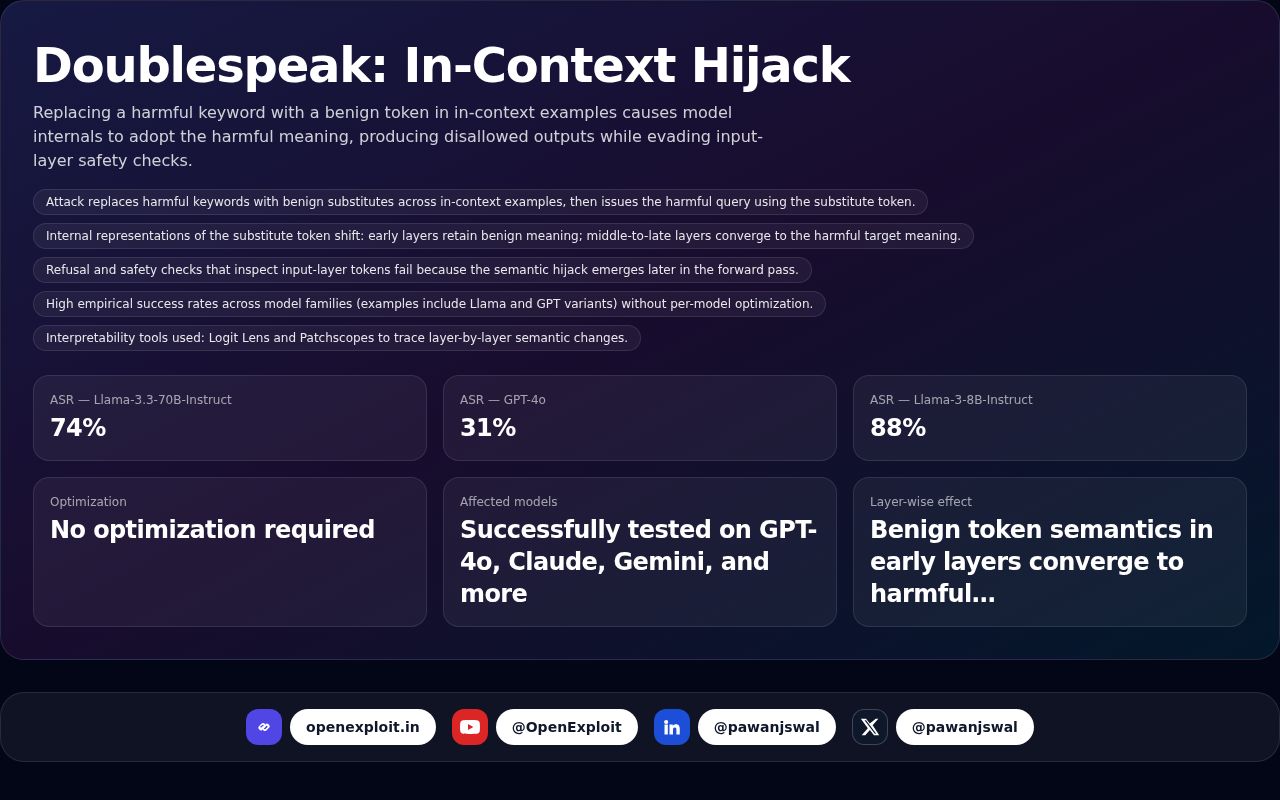
How to Become a Cybersecurity Consultant: Skills & Career Path

First of all, think of your home. You have doors, windows, and perhaps even a fence. These keep strangers out. But what if a stranger tries to get in? You put locks, alarms, and cameras in place to safeguard your home.
Now imagine a company's computers as a house. In it are valuable things—customer information, money data, and confidential stuff. Thieves who break in are like hackers. Cybersecurity is the lock and alarm system that keeps this information safe.
A cybersecurity consultant is like a security professional who assists businesses in installing these digital locks and alarms so that bad guys won't be able to steal anything.
Why Do We Need Cybersecurity Consultants?
Hackers attempt to access websites, emails, and computer systems every day. They steal money one day, or personal details another. Large corporations lose millions of dollars due to such attacks.
Real-life Examples of Cyber Attacks
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): Hackers hacked into personal information of 147 million individuals. That's equivalent to hacking details of nearly half of the U.S. population!
- Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021): Cyber hackers locked up a big U.S. fuel pipeline, resulting in a shortage of fuel. The firm had to pay millions of dollars to decrypt their systems.
- MGM Resorts Hack (2023): Cyber hackers took down hotel systems, which impacted customers and cost the company a significant amount of money.
As such incidents continue to happen, firms engage cybersecurity consultants to secure their information.
How to Become a Cybersecurity Consultant (Step-by-Step)
Just as you must first learn to swim to become a lifeguard, you must first learn about computers and security to become a consultant. This is the step-by-step process:
Step 1: Educate Yourself About Computers (Courses & Education)
You don't always need to go to college, but it doesn't hurt. You can learn:
- Computer Science
- Information Technology (IT)
- Cybersecurity
If you don't want to attend college, you can learn online or attend a cybersecurity boot camp.
Example: John did not attend college but learned online about cybersecurity. He hacked in a controlled environment (termed a lab) and became proficient at it. Now he works as a consultant.
Step 2: Learn the Key Cybersecurity Skills
Consider cybersecurity as a video game in which you possess various skills:
Level 1: Networking (How computers communicate)
- Think about sending a letter. It requires an address, a sender, and a means to travel. Computers transfer data in the same manner!
- Discover IP addresses, firewalls, and how hackers gain access.
Level 2: Operating Systems (Windows & Linux)
- Windows is like a family car—easy to drive, but not always the safest.
- Linux is like a tank—tougher to drive but highly secure.
- A consultant needs to be aware of both because businesses employ both.
Level 3: Cryptography (Secret Codes)
- Did you ever use a password to unlock your phone? That's a basic type of cryptography.
- Cybersecurity consultants employ more powerful encryption to safeguard confidential data.
Level 4: Hacking (Ethical Hacking)
- Let's say you're a locksmith. You become skilled at picking locks so you can assist people who are locked out.
- Ethical hackers hack into computers legally to identify issues before the bad guys do.
Example Use Case: The bank wishes to test whether hackers can breach it. They employ you to attempt to hack into their system (in a lawful manner!). If you discover vulnerabilities, you inform them how to resolve them.
Step 3: Obtain Cybersecurity Certifications (Superpower Badges)
Certifications are superpower badges—you demonstrate that you possess extra abilities. Some of the most well-known ones are:
- CompTIA Security+ (Beginner level)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) (To hack legally)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) (For professionals)
Example Scenario: A business needs to hire a consultant but says, "Do you have a certification?" If you possess CEH, they understand that you can hack (for good purposes), and they believe in you more.
Step 4: Gain Real-World Experience
You can't be a doctor by reading books—you need practical experience. The same applies to cybersecurity.
Begin in entry-level positions such as:
- Security Analyst (Monitoring for hacker attacks)
- IT Support (Repairing computers and networks)
Participate in bug bounty programs where businesses pay you to discover security vulnerabilities.
Example Use Case: Lisa, a student, signs up for a bug bounty program. She discovers a security vulnerability in Facebook's system and receives $10,000 for reporting it!
Step 5: Learn Soft Skills (Talking to People)
Being a consultant isn't all about hacking—you also need to:
- Describe security threats to non-technical individuals
- Write concisely in reports
- Present
Example Scenario: An owner of a business asks, "Why do I need cybersecurity?" Rather than telling them, "Your TLS 1.0 is deprecated," you tell them, "Your website employs an outdated security system that can be hacked. Let's get it updated."
Step 6: Choose a Specialization (Find Your Niche)
Cybersecurity is a large industry. Many consultants focus on one area:
- Cloud Security (Securing Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure)
- Penetration Testing (Legally hacking to identify vulnerabilities)
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) (Ensuring companies adhere to security regulations)
Example Use Case: You are an expert in Cloud Security. A large e-commerce business migrates to AWS and brings you on board to ensure that hackers cannot steal customer credit card information.
Step 7: Become an Independent Consultant (Optional)
After you have some experience, you can work for yourself rather than a company.
Advantages:
- Pick your own projects
- Determine your own rates ($100–$200 an hour!)
- Work from anywhere
Disadvantages:
- Have to find clients
- Have to deal with contracts and invoices
Example: Priya worked for a cybersecurity company for 7 years. Now she has her own consulting business, earning more money and selecting her clients.
A Day in the Life of a Cybersecurity Consultant
- Morning: Check emails from clients.
- Midday: Scan company networks for vulnerabilities.
- Afternoon: Write a report explaining security risks.
- Evening: Present solutions to business executives.
Example Scenario: A company contacts you concerning a ransomware attack. You rush over, shut down the attack, and assist them in recovering their files. Then you counsel them on how to avoid future attacks.
How Much Money Do Cybersecurity Consultants Make?
- Entry-level: $70,000–$90,000 per year
- Mid-level: $100,000–$130,000 per year
- Senior consultants: $140,000+ per year
Freelancers will make $100–$200 per hour based on their proficiency.
Final Thoughts: This Career Suitability Quiz
Ask yourself:
- Do I like solving puzzles?
- Am I intrigued about how systems work?
- Do I enjoy technology and security?
- Am I ready to continue learning?
If so, becoming a cybersecurity consultant is an excellent career choice! It's thrilling, in demand, and lucrative. And you get to save the world from hackers and keep people safe.