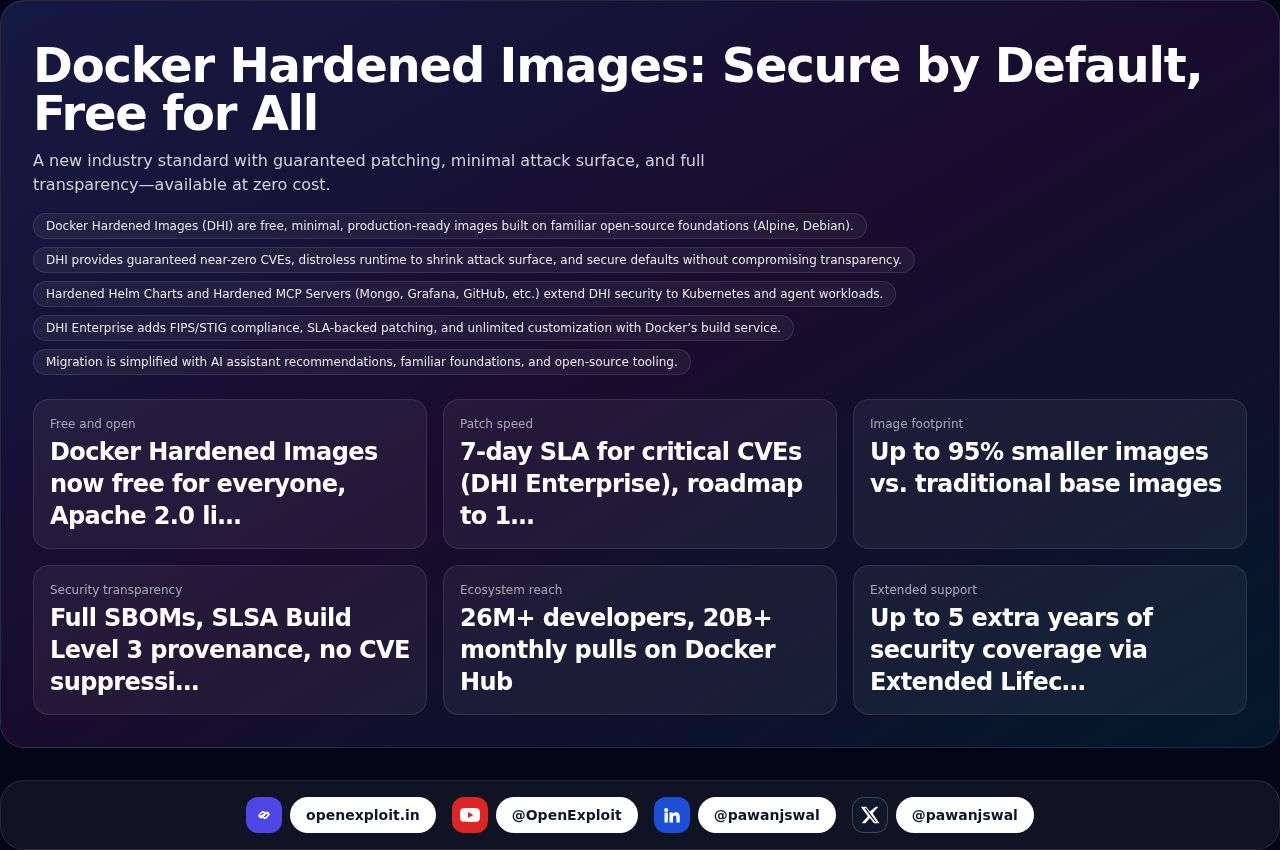
Fuzzy Canary
A lightweight tool that injects invisible 'canary' links into your HTML to trigger scrapers' content safeguards. Install via npm and prefer server-side injection so non-JS scrapers still see it.
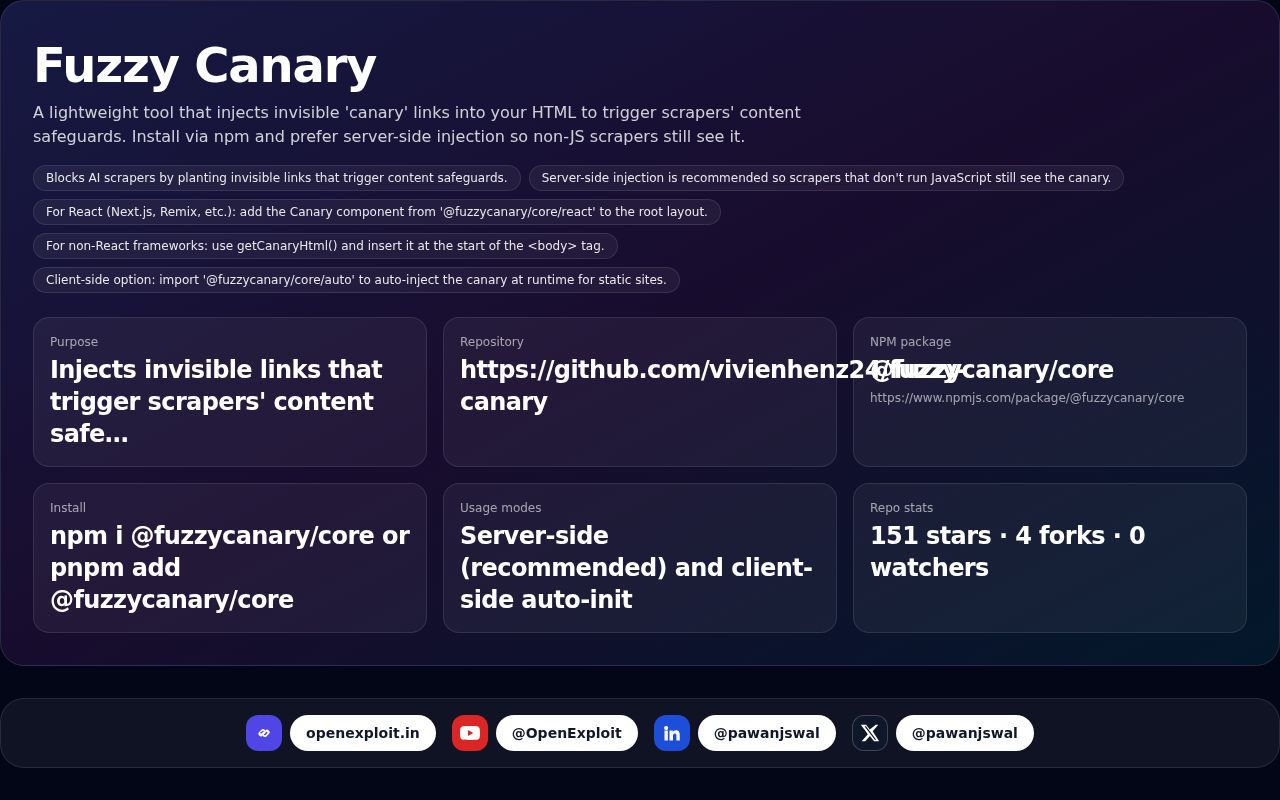
Tired of AI scrapers hoovering your blog? Plant a canary in your HTML that makes scrapers think twice.
A lightweight tool that injects invisible 'canary' links into your HTML to trigger scrapers' content safeguards. Install via npm and prefer server-side injection so non-JS scrapers still see it.
Source: GitHub — vivienhenz24/fuzzy-canary — Source link
Highlights
| Metric | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Injects invisible links that trigger scrapers' content safeguards | |
| Repository | https://github.com/vivienhenz24/fuzzy-canary | |
| NPM package | @fuzzycanary/core | https://www.npmjs.com/package/@fuzzycanary/core |
| Install | npm i @fuzzycanary/core or pnpm add @fuzzycanary/core | |
| Usage modes | Server-side (recommended) and client-side auto-init | |
| Repo stats | 151 stars · 4 forks · 0 watchers |
Key points
- Blocks AI scrapers by planting invisible links that trigger content safeguards.
- Server-side injection is recommended so scrapers that don't run JavaScript still see the canary.
- For React (Next.js, Remix, etc.): add the Canary component from '@fuzzycanary/core/react' to the root layout.
- For non-React frameworks: use getCanaryHtml() and insert it at the start of the <body> tag.
- Client-side option: import '@fuzzycanary/core/auto' to auto-inject the canary at runtime for static sites.
- Tool injects for every visitor including crawlers—test in staging before rolling out to production.
- Open-source README with license and npm package available.
Why this matters
As AI models scrape public sites for training, site owners lose control of their content. Fuzzy Canary offers a pragmatic, low-cost way to deter automated scrapers by exploiting content safeguards — but it can affect indexing, so validate in staging and weigh SEO trade-offs before production use.